消息的处理最终会调用ActivityThread类的某个方法完成。
通过这种模式,从Binder来的调用就转换成异步的方式来执行了。理解了这个过程之后,再分析ApplicationThread类的接口是时,我们可以忽略中间的消息传递过程,直接查看ActivityThread中对应的方法。
由此我们可以得到ActivityThread框架图:
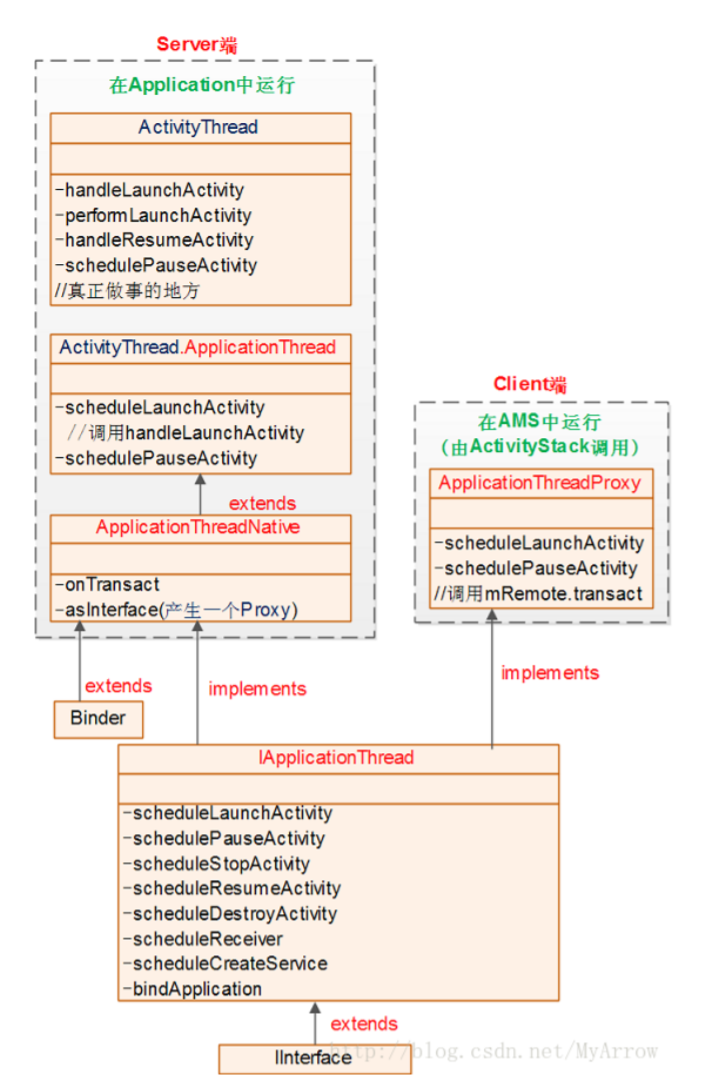
通常ApplicationThread中的接口方法都是以“schedule”开头,而ActivityThread中对
应的处理方法则以“handle”开头。
Activity的创建并回调onCreate()
ActivityThread中的成员变量mActivities中保存了所有ActivityClientRecord对象,该类中重要
的成员变量如下:
static final class ActivityClientRecord {
IBinder token; // Activity对象的全局唯一标示
Intent intent; // 启动Activity的Intent
Activity activity; // Activity对象
Window window; // Activity的窗口对象
boolean paused; // 是否在暂停状态的标志
boolean stopped; // 是否在停止状态的标志
ActivityInfo activityInfo; // Activity的信息
LoadedApk packageInfo; // 包的信息
}
token的类型是IBinder,在ActivityManagerService中会为每个应用程序中的Activity对象建立
了一个对应的ActivityRecord对象,ActivityRecord会创建一个token对象来作为Activity的标
识。这个token是个Binder对象,但是它不是为提供Binder服务而创建的,这里只是利用
Binder对象的 系统全局唯一性 来作为标识符。
每一个Activity都包含了一个Window对象,Window对象关联着应用框架的一大块内容。
从上面的框架图我们可以得知:启动一个Activity,首先会经过AMS和ActivityThread之间又长
又臭的调用和回调,最终才会调到ActivityThread的handleLaunchActivity()方法。下面我们看
一下接下来的流程。
handleLaunchActivity
/**
* Extended implementation of activity launch. Used when server requests a launch or relaunch.
*/
@Override
public Activity handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r,
PendingTransactionActions pendingActions, Intent customIntent) {
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
if (r.profilerInfo != null) {
mProfiler.setProfiler(r.profilerInfo);
mProfiler.startProfiling();
}
// Make sure we are running with the most recent config.
handleConfigurationChanged(null, null);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Handling launch of " + r);
// Initialize before creating the activity
if (!ThreadedRenderer.sRendererDisabled
&& (r.activityInfo.flags & ActivityInfo.FLAG_HARDWARE_ACCELERATED) != 0) {
HardwareRenderer.preload();
}
WindowManagerGlobal.initialize();
// Hint the GraphicsEnvironment that an activity is launching on the process.
GraphicsEnvironment.hintActivityLaunch();
// 执行Activity创建和onCreate流程
final Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);
if (a != null) {
r.createdConfig = new Configuration(mConfiguration);
reportSizeConfigurations(r);
if (!r.activity.mFinished && pendingActions != null) {
pendingActions.setOldState(r.state);
pendingActions.setRestoreInstanceState(true);
pendingActions.setCallOnPostCreate(true);
}
} else {
// If there was an error, for any reason, tell the activity manager to stop us.
try {
ActivityTaskManager.getService()
.finishActivity(r.token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
Activity.DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
return a;
}handleLaunchActivity()再调用performLaunchActivity()方法来创建Activity并执行onCreate流
程,返回后再执行Activity的onResume流程。
/** Core implementation of activity launch. */
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
// 首先,从ActivityClientRecord中获取待启动的Activity的组件信息
ActivityInfo aInfo = r.activityInfo;
// 获取Activity的packageInfo
if (r.packageInfo == null) {
r.packageInfo = getPackageInfo(aInfo.applicationInfo, r.compatInfo,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
}
// 获取Activity的ComponentName
ComponentName component = r.intent.getComponent();
if (component == null) {
component = r.intent.resolveActivity(
mInitialApplication.getPackageManager());
r.intent.setComponent(component);
}
if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null) {
component = new ComponentName(r.activityInfo.packageName,
r.activityInfo.targetActivity);
}
ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
Activity activity = null;
try {
// 拿到加载Activity的ClassLoader, 创建Activity对象
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
try {
// 拿到当前进程中的Application对象
Application app = r.packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Performing launch of " + r);
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, r + ": app=" + app
+ ", appName=" + app.getPackageName()
+ ", pkg=" + r.packageInfo.getPackageName()
+ ", comp=" + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString()
+ ", dir=" + r.packageInfo.getAppDir());
if (activity != null) {
CharSequence title = r.activityInfo.loadLabel(appContext.getPackageManager());
Configuration config = new Configuration(mCompatConfiguration);
if (r.overrideConfig != null) {
config.updateFrom(r.overrideConfig);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Launching activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with config " + config);
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
// Activity resources must be initialized with the same loaders as the
// application context.
appContext.getResources().addLoaders(
app.getResources().getLoaders().toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]));
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback,
r.assistToken);
if (customIntent != null) {
activity.mIntent = customIntent;
}
r.lastNonConfigurationInstances = null;
checkAndBlockForNetworkAccess();
activity.mStartedActivity = false;
int theme = r.activityInfo.getThemeResource();
if (theme != 0) {
activity.setTheme(theme);
}
activity.mCalled = false;
if (r.isPersistable()) {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state, r.persistentState);
} else {
mInstrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(activity, r.state);
}
if (!activity.mCalled) {
throw new SuperNotCalledException(
"Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +
" did not call through to super.onCreate()");
}
r.activity = activity;
mLastReportedWindowingMode.put(activity.getActivityToken(),
config.windowConfiguration.getWindowingMode());
}
r.setState(ON_CREATE);
// updatePendingActivityConfiguration() reads from mActivities to update
// ActivityClientRecord which runs in a different thread. Protect modifications to
// mActivities to avoid race.
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
mActivities.put(r.token, r);
}
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to start activity " + component
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
}
return activity;
}从上面代码我们发现,ActivityThread最后调用了mInstrumentation变量的newActivity()方法来
创建Activity对象,并回调了callActivityOnCreate()方法,走完Activity的onCreate流程。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java
/**
* Perform calling of an activity's {@link Activity#onCreate}
* method. The default implementation simply calls through to that method.
*
* @param activity The activity being created.
* @param icicle The previously frozen state (or null) to pass through to onCreate().
*/
public void callActivityOnCreate(Activity activity, Bundle icicle) {
prePerformCreate(activity);
activity.performCreate(icicle);
postPerformCreate(activity);
} frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java
@UnsupportedAppUsage
final void performCreate(Bundle icicle, PersistableBundle persistentState) {
dispatchActivityPreCreated(icicle);
mCanEnterPictureInPicture = true;
// initialize mIsInMultiWindowMode and mIsInPictureInPictureMode before onCreate
final int windowingMode = getResources().getConfiguration().windowConfiguration
.getWindowingMode();
mIsInMultiWindowMode = inMultiWindowMode(windowingMode);
mIsInPictureInPictureMode = windowingMode == WINDOWING_MODE_PINNED;
restoreHasCurrentPermissionRequest(icicle);
if (persistentState != null) {
onCreate(icicle, persistentState);
} else {
onCreate(icicle);
}
EventLogTags.writeWmOnCreateCalled(mIdent, getComponentName().getClassName(),
"performCreate");
mActivityTransitionState.readState(icicle);
mVisibleFromClient = !mWindow.getWindowStyle().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.Window_windowNoDisplay, false);
mFragments.dispatchActivityCreated();
mActivityTransitionState.setEnterActivityOptions(this, getActivityOptions());
dispatchActivityPostCreated(icicle);
}
这样Activity在应用端进程ActivityThread的启动流程和生命周期回调流程都简单分析完了。
小结一下 :
AMS通过Binder进行IPC通讯,通知应用进程ActivityThread启动指定Activity
调用ApplicationThread.scheduleLaunchActivity()。
经过Handler消息传动,调用ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity()。
调用ActivityThread.performLaunchActivity()完成Activity的加载,并最终调用Activity生
命周期的onCreate()方法
performLaunchActivity返回,继续调用ActivityThread.handleResumeActivity(),该方法
内部又调用ActivityThread.performResumeActivity(),其内部仅仅调用了目标Activity的
onResume()方法。到此Activity启动完成。
Activity的其他生命周期方法onRestart等,可以根据onCreate流程为类推,举一反三。




近期评论